Why Your Clients Should Move to the Cloud
There are a lot of reasons to move to the Cloud. Rattling them off sounds like a CEO’s wish list – cost savings, efficiency, increased collaboration, data security, dynamic scalability, in-the-moment upgrades/updates, improved resource utilization, connection of a dispersed workforce, rapid deployment, redundancy for storage/backup/recovery, and collecting information/analytics/intelligence. Essentially, do more while paying less.
Position to be competitive. With cloud, your customers’ workforce, markets, and opportunities are not tied to a physical structure or location. Organizations can recruit the best prospects regardless of where they live, take advantage of cost savings a dispersed operation can provide, and be able to work with customers, with the full might of their dispersed organization, anywhere in the world.
Data empowered. More is usually better. It’s true in this case. With more information organizations gain deeper intelligence about their workings, processes, and customers. Access to analytics allows organizations to make smarter decisions and find potential surprises that can change their roadmap for the future. The more they know, the more they can do. Knowing customer behavior can lead to improved sales and retention. Seeing an opportunity to improve processes can save time and money. Not having these key findings leaves your customers in a reactive state, or even worse, unaware.
Target Your Cloud Conversation with the Services they Need
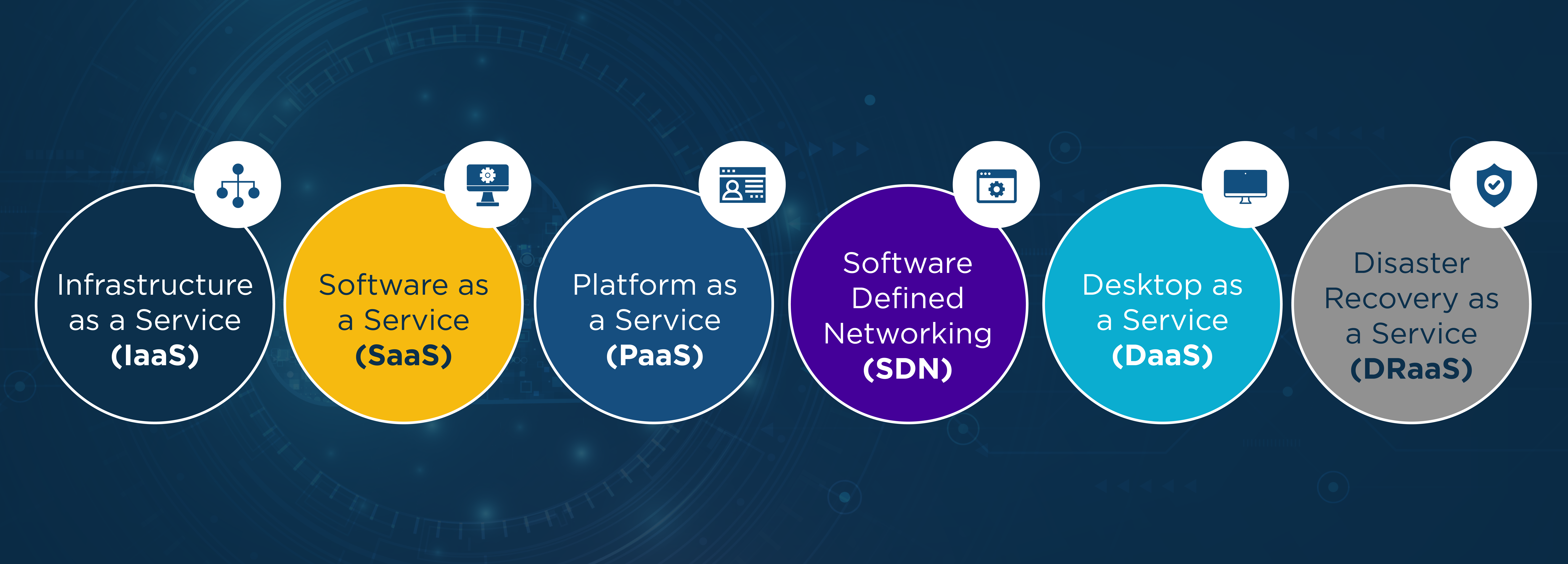
Narrowing the scope of your conversation with the customer can often bring clarity. To speed the process along, introduce cloud services by industry standardized categories:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides a virtualized platform to support your customer’s operations – often paired with Hardware as a Service (HaaS) which encompasses the hardware, software, storage, data center, servers, and network space requirements.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) allows your customers to purchase access to applications owned and managed by a vendor, hosted in the Cloud, and accessed with web-passed technology via a browser or app.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a middle ground between IaaS and SaaS. Often reserved for application development, it contains the database managements systems and programming language libraries technical teams require to develop, run, and manage applications.
- Software Defined Networking (SDN), or SD-WAN (Software Defined Wide-Area Network), is often used with Cloud since it gives redundancy, quality of experience, etc.
- Desktop as a Service (DaaS) securely delivers virtual apps and desktops, often via subscription, from the Cloud to any device. The provider takes care of backend management reducing expense, minimizing resource expenditure, and removing the need for staffing oversight.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) backups data and IT infrastructure to a third-party Cloud computing environment with protocols in place should the main system be compromised. If an event occurs, the data is protected, ready to be restored with limited downtime.
Common Cloud Deployment Methods

There are many deployment models out there, and they could easily warrant a blog post on their own. Keeping to the “Primer” model, we will quickly look at the 4 most common types, which are:
- Public Cloud allows your customer to share resources, and offers services to the public over the Internet. Typically, they are very scalable horizontally, with the ability to take things up and down very quickly and add resources as needed. You can think of this method as “Hyperscalers” due to this flexibility – great examples include AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Private Cloud, also known as Single Tenant, is where one organization operates all on the same hardware. There are options for off-premise or on-premise deployment solutions. Tierpoint, Flexential, and Rackspace are all great options for this approach.
- Hybrid Cloud provides organizations with a different, but very dynamic approach, with some aspects kept on the premises or in a colocation facility, while others are running on a public Cloud infrastructure. There can be crossover, redundancy, or dedicated processes. Flexibility is always a function of the Cloud. Datacenter providers often tie to one of the hyperscalers, with AWS, Azure, and GCP again being excellent choices.
- Multi-Tenant Cloud approach, typically based on vmware or hyper-v platforms, gives organizations access to the best CPU, RAM, and storage on well-known hypervisors (the software that creates and runs virtual machines). The Cloud network is still private, but, like a condominium, lets each tenant enjoy shared elements without assuming the full budgetary burden. Great providers include Tierpoint, Rapidscale, EvolveIP, Flexential, and Effortless Office.
How Cloud Technology Works – What You See, And What You Don’t
Intuitively, most people can understand the difference between front and back end, the terms are used in everyday language. That being said, terms that exist in the everyday vernacular can become fuzzy over time, and should be defined to avoid any misunderstanding. Here’s what you should know:
- Front End, is the portion that the customer (or end user), actually sees and interacts with through a digital device via browser or standalone app. It’s this GUI (Graphical User Interface) that is clicked on to navigate through information, and actionable commands…like what’s seen when browsing Facebook. Think of it as the access point, connected via the internet, that receives and works with the resources. The front end will often include digital devices, networks, and browsers/apps.
- Back End, is the database and other logic that sits behind the customer/user experience (front end). This includes the data storage systems, Cloud-based applications, logic, workflow design, and shared/dedicated servers that are the backbone of the Cloud – and ultimately responsible for Cloud performance, and the interaction experience.
Learn more by re-watching our Webinar “The Cloud is the Future, Make Sure You’re the Expert Your Customers Need” featuring SVP of Sales Engineering Gerry Davis and a panel of experts from top Cloud providers.
Our team is always here to help you expand your Cloud business!
Our Featured Providers
TierPoint is a leading national provider of hybrid IT, helping organizations drive performance and manage risk. The company has over 5,000 clients ranging from the public to private sectors, from small businesses to Fortune 500 enterprises. TierPoint also has one of the largest and most geographically diversified footprints in the nation, with 40 world-class data centers in 20 markets and 8 multi-tenant cloud pods, connected by a coast-to-coast network. They offer a comprehensive solution portfolio of private, multitenant, hyperscale, and hybrid cloud, plus colocation, disaster recovery, security, and other managed IT services. Led by a proven management team, TierPoint’s network of hundreds of highly experienced IT professionals offer local, white-glove customer service, seamlessly managing and customizing agile solutions that address each client’s unique needs.
Data Canopy is a nationwide hybrid infrastructure provider. They reduce the cost and complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments by connecting, storing, and securing physical and virtual infrastructure under one invoice. Custom-fit data center solutions ensure customers are getting the infrastructure, network, redundancy, and security that best support their data and business needs now, and as they grow.
Zayo provides communications Infrastructure services, including fiber and bandwidth connectivity, colocation and cloud services to the world’s leading businesses. Customers include wireless and wireline carriers, media and content companies and finance, healthcare and other large enterprises. Zayo’s 127,000-mile network in North America and Europe, includes extensive metro connectivity to thousands of buildings and data centers. In addition to high-capacity dark fiber, wavelength, Ethernet and other connectivity solutions, Zayo offers colocation and cloud infrastructure in its carrier-neutral data centers. Zayo provides clients with flexible, customized solutions and self-service through Tranzact, an innovative online platform for managing and purchasing bandwidth and services.
RapidScale, is a managed cloud services provider, delivers world-class, secure, and reliable cloud computing solutions to companies of all sizes across the globe. It’s managed CloudDesktop platform and market-leading cloud solutions enable RapidScale to innovate advanced solutions and applications for cloud computing. RapidScale’s services include CloudServer, CloudDesktop, CloudOffice, CloudMail, CloudRecovery, CloudApps, and more.
Rackspace is a leading end-to-end multi-cloud solutions expert. They combine expertise with the world’s leading technologies- across applications, data, and security. As a global, multi-cloud technology services provider, Rackspace delivers innovative capabilities of the cloud to help customers build new revenue streams, increase efficiency, and create incredible experiences. Rackspace has deep expertise on AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud or GCP, VMware, Kubernetes, Oracle, SAP, Salesforce, and many other industry-leading technologies.
Sandler Partners have access to the full portfolio of 160+ Cloud solutions — including leading providers Flexential, EvolveIP, Effortless Office, PheonixNAP, Nitel, and Comcast/Masergy. You can review all your available options by using the Solutions Finder or Solutions Index tools located in the Sandler Portal. For help navigating your way through the process, while discovering the best provider(s) solutions available to meet your client’s requirements, simply contact our Sales Engineering Team!